Sunroof vs moonroof sets the stage for a deep dive into the fascinating world of automotive design choices. This exploration delves into the nuances of these popular features, comparing their design, functionality, and impact on a vehicle’s overall appeal.
Both sunroofs and moonroofs offer a connection to the outdoors, but their design and function differ subtly. Understanding these differences is crucial for car buyers seeking the best fit for their needs and preferences.
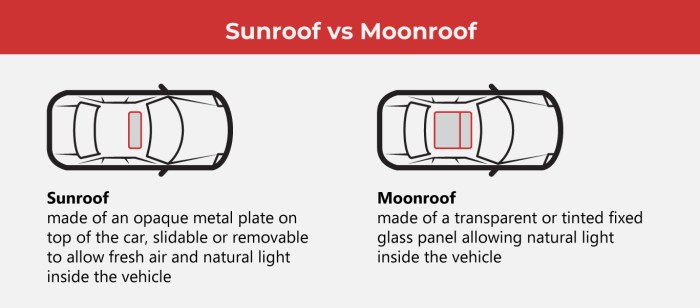
Introduction to Sunroof vs. Moonroof
Sunroofs and moonroofs, both offering a connection to the sky, are popular features in modern vehicles. While both allow natural light and fresh air into the cabin, subtle design differences contribute to distinct experiences. Understanding their historical development, design specifics, and common misconceptions is key to choosing the right option for your needs.A sunroof is a full, often panoramic, opening in the roof, extending from one side of the vehicle to the other.
A moonroof, conversely, is a smaller, typically fixed-position opening, resembling a hinged window, situated more centrally on the roof. These variations in design stem from the differing engineering challenges presented by each. The evolution of both sunroof and moonroof technology has been driven by consumer demand for greater interior comfort and improved vehicle aesthetics.
Historical Context
The development of sunroofs and moonroofs mirrors the broader advancements in automotive engineering. Early models featured limited skylight options, often in the form of small, fixed windows. The 1950s saw the beginnings of electrically powered, operable sunroofs in some luxury vehicles, a trend that gradually expanded to other segments of the market. Moonroofs, typically a later addition, offered a more compact and cost-effective alternative for providing natural light and ventilation.
This evolution was directly influenced by the need for better interior comfort and the rising demand for aesthetic upgrades.
Design and Functionality Differences
The fundamental difference lies in the size and opening mechanism. Sunroofs typically span the entire roofline, offering a wider expanse of natural light and a larger opening for ventilation. Moonroofs, conversely, are smaller, often positioned centrally and are typically fixed or hinged, which may be a drawback for those seeking ample air circulation. This difference in design also translates to varying levels of noise insulation.
Common Misconceptions
A common misconception is that sunroofs are inherently superior to moonroofs. The suitability of either depends entirely on the desired level of natural light, ventilation, and the overall design aesthetic of the vehicle. A smaller moonroof can still effectively serve the purpose of providing some daylight and ventilation, while a larger sunroof offers a more expansive connection to the outdoors.
Cost Considerations
The manufacturing and installation of sunroofs typically involve more complex engineering, leading to higher production costs compared to moonroofs. This difference in cost is often reflected in the final retail price of the vehicle.
Design and Construction
Sunroofs and moonroofs, while seemingly similar, differ significantly in their structural engineering and material choices. These differences affect their performance, durability, and overall functionality within the vehicle’s design. Understanding these nuances helps appreciate the intricacies of automotive engineering.The structural integrity of a sunroof or moonroof is paramount. Design engineers must account for the added weight and potential stress points on the roof, ensuring the opening mechanism can withstand regular use and potential impacts.
This necessitates careful calculations and rigorous testing to guarantee passenger safety and vehicle longevity. Different manufacturers employ varying strategies to meet these requirements, reflecting their specific design philosophies and engineering approaches.
Structural Engineering Considerations
The structural engineering of sunroofs and moonroofs necessitates careful consideration of load distribution and stress points. Sunroofs, typically smaller and often integrated into the roof’s existing structural framework, encounter less complex stress scenarios. Moonroofs, often larger and with a more independent design, demand a more elaborate structural support system to accommodate the greater surface area and potential forces. This necessitates reinforced bracing and support structures around the opening, ensuring stability during operation and over time.
Materials and Performance
The materials used in sunroof and moonroof construction play a crucial role in their performance. A critical aspect involves balancing the need for strength and rigidity with lightweight construction. Common materials include high-strength steel alloys, aluminum, and various types of reinforced polymers. Aluminum, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, is frequently employed in modern designs, contributing to improved fuel efficiency.
Polymers, though lighter, require careful engineering to ensure they can withstand the stresses of operation. The selection of specific materials also affects the overall weight of the vehicle and its impact on fuel economy.
Glass Types and Properties
The glass used in sunroofs and moonroofs significantly influences the overall performance. Different types of glass are available, each with unique properties, including: insulating glass, laminated glass, and tempered glass. Insulating glass, composed of multiple panes with a gas-filled space between them, reduces heat transfer, enhancing thermal comfort. Laminated glass, with a thin interlayer, enhances safety by improving impact resistance.
Tempered glass, strengthened through a heat treatment process, further improves safety by increasing its resistance to breakage. The choice of glass type directly impacts the vehicle’s thermal efficiency, safety features, and overall aesthetics.
Manufacturer and Model Variations, Sunroof vs moonroof
Manufacturers often implement unique design solutions for their sunroofs and moonroofs, tailored to specific vehicle models. These variations can include different opening mechanisms, glass types, and frame configurations. For example, some manufacturers might prioritize a sleek design by incorporating hidden hinges or compact actuators. Others might emphasize safety by employing advanced impact-resistant glass. Observing these differences across various models highlights the adaptability of automotive design principles to cater to specific aesthetic and functional requirements.
Functionality and Features
Sunroofs and moonroofs, while both offering a connection to the outdoors, vary significantly in their functionality and features. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate option for a vehicle’s intended use and aesthetic preferences. These variations influence the overall driving experience and the vehicle’s visual appeal.The functionality of a sunroof or moonroof extends beyond simply letting in natural light.
Power operation, drainage systems, and sealing contribute to the user experience and vehicle performance. These features, combined with aesthetic considerations, can significantly impact the overall appeal and desirability of a vehicle.
Sunroofs and moonroofs offer different aesthetics, but for long EV road trips, the practicality of a sunroof is key. Open-air driving in an electric vehicle, especially on scenic routes, is a fantastic experience, but consider the extra headroom and visibility benefits a sunroof provides during those EV road trips. Ultimately, the best choice depends on personal preference and the specific features of the vehicle, though.
A sunroof might be more useful than a moonroof, especially on extended EV journeys.
Power Operation
Power-operated sunroofs and moonroofs offer convenience and safety. Electric actuators allow for easy opening and closing, typically with adjustable settings for ventilation. This feature is especially appreciated in warm climates for temperature regulation and in colder weather to avoid sudden drafts. Manual models, though often more budget-friendly, require manual effort and can be less convenient.
Drainage Systems
Proper drainage is essential for both types of roofs to prevent water from accumulating and causing damage. Advanced systems utilize channels and grooves to direct rainwater away from the vehicle’s interior. Effective drainage is critical for maintaining the vehicle’s structural integrity and preventing water leaks or damage. A well-designed drainage system is less likely to lead to water intrusion issues, protecting the vehicle’s components and ensuring the driver’s comfort.
Sealing and Weatherproofing
The sealing and weatherproofing of sunroofs and moonroofs are crucial for preventing leaks and maintaining a comfortable interior environment. High-quality seals and gaskets play a vital role in keeping out wind, rain, and debris. Modern vehicles utilize advanced materials and construction techniques to minimize the risk of leaks and ensure a reliable seal. Effective sealing is paramount for preventing moisture damage, maintaining interior comfort, and enhancing the overall durability of the vehicle.
Aesthetic Enhancement
Both sunroofs and moonroofs can significantly enhance a vehicle’s aesthetics. The design and size of each type of roof can influence the overall look and feel of the car. Sunroofs can contribute to a sense of spaciousness and a modern aesthetic, while moonroofs often provide a more sophisticated and integrated appearance. The choice of roof style often correlates with the vehicle’s intended market segment and overall design philosophy.
Performance and Advantages

Sunroofs and moonroofs, while both offering views and natural light, differ significantly in their performance characteristics. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the appropriate option based on individual needs and priorities. Factors like air circulation, temperature regulation, noise levels, and wind resistance all play a part in the overall experience.The performance advantages and disadvantages of each type are intricately linked to their design and construction.
Careful consideration of these factors allows for a more informed decision-making process.
Light and Air Circulation
Sunroofs, typically larger than moonroofs, generally provide greater light and air circulation. This is due to their wider opening and often more complex design. Moonroofs, conversely, while offering a view to the sky, often have a more limited ability to allow substantial air flow. This can be significant in climates with high humidity or intense sunlight, where a sunroof may be more desirable for optimal ventilation.
Interior Temperature Regulation
The impact on interior temperature regulation is closely tied to light and air circulation. Sunroofs, with their larger opening, can effectively cool down the interior, particularly in hot weather, by allowing a greater exchange of air. Moonroofs, with their more contained opening, may not have the same cooling effect. Moreover, the orientation and design of the sunroof can contribute to reducing solar heat gain, enhancing the efficiency of temperature regulation.
Noise Levels and Wind Resistance
Sunroofs, due to their larger size and often more exposed design, are more susceptible to noise from wind and road. Moonroofs, with their smaller, more enclosed design, tend to reduce wind noise and turbulence. The quality of the sealing mechanisms around the sunroof significantly influences the amount of noise that penetrates the cabin. Specific models and their design features often affect these performance metrics, with some manufacturers implementing noise-reduction technologies in their sunroof designs.
Performance Metrics
| Feature | Sunroof | Moonroof |
|---|---|---|
| Noise Reduction (dB) | Typically 65-75 dB (depending on model and driving conditions) | Typically 60-70 dB (depending on model and driving conditions) |
| Airflow (m³/hr) | Potentially higher, varying by design. | Lower, varying by design. |
| Heat Rejection (BTU/hr) | Can be higher with efficient design and glass coatings | Lower heat rejection, varying by design. |
Note: These are general ranges and specific values vary significantly based on the vehicle model, design features, and operating conditions.
For example, a luxury sedan might boast a sunroof with advanced noise-reducing seals and a sophisticated glass coating to minimize solar heat gain, leading to superior performance in these areas compared to a compact car with a standard sunroof.
Installation and Maintenance
Installation and maintenance procedures for sunroofs and moonroofs vary based on the vehicle make and model, and the specific design of the opening mechanism. Understanding these nuances is crucial for ensuring proper functionality and longevity. Differences in installation complexity and maintenance requirements contribute to the varying costs associated with each type.
Installation Procedures
The installation of sunroofs and moonroofs typically involves specialized tools and techniques. Professional installation is recommended for both types to ensure proper sealing, alignment, and operation. DIY installation can be challenging and potentially lead to leaks, malfunctions, or damage to the vehicle’s interior. Skilled technicians are trained to properly secure the components, ensuring a tight seal that prevents water intrusion.
Thorough inspection of the surrounding components like the roof frame and seals is crucial during the installation process. Sunroof installation often involves careful alignment and sealing of the glass panel to prevent air leaks and water intrusion. Moonroof installation generally involves a more complex alignment process due to the design of the opening mechanism.
Maintenance Requirements
Regular maintenance is essential for maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of sunroofs and moonroofs. This includes routine cleaning and inspections to prevent corrosion, leaks, and mechanical issues. Regular cleaning of the glass and frame is crucial for maintaining a clear view and preventing debris buildup. Checking for any signs of leaks, such as water spots or dampness, is also essential.
Lubrication of moving parts is crucial for smooth operation and extended lifespan. Checking for any signs of wear and tear, such as cracks or damage to the seals, is vital to prevent future issues.
Cost Comparison
The costs associated with installation and maintenance for sunroofs and moonroofs can vary significantly. Professional installation for a sunroof can range from $500 to $2,000, depending on the complexity of the vehicle and the specific sunroof model. A moonroof installation can cost between $700 and $3,000. Ongoing maintenance, such as cleaning and lubrication, is generally less expensive than installation, costing between $25 and $100 annually.
Factors like the frequency of use and the quality of the components used influence the overall maintenance cost.
Potential Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Sunroofs and moonroofs can experience various issues, including leaks, malfunctions, and damage to seals. Leaks are a common problem that can arise from improper installation or wear and tear on seals. Malfunctions can stem from issues with the electric motor, sensors, or other components. Troubleshooting tips include checking for any visible signs of water intrusion, inspecting seals for damage, and checking the electrical connections.
If a leak is suspected, inspect the drain channels and ensure they are clear. If a malfunction occurs, consult a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair the issue. Using specialized cleaning solutions for the glass can prevent scratching and maintain a clear view.
Cost and Value Proposition
The price difference between sunroofs and moonroofs often reflects the design complexity and manufacturing processes involved. Understanding the factors influencing these costs is crucial to assessing the value proposition of each option for a vehicle buyer. A thorough comparison of the value proposition and the impact on resale value allows informed decisions.Typically, sunroofs are more expensive than moonroofs due to their larger size and more intricate construction.
This difference in cost directly affects the overall value proposition, impacting the potential return on investment when considering a vehicle purchase.
Price Difference Analysis
Sunroofs generally command a higher price tag than moonroofs. This is primarily attributed to their larger surface area, requiring more material and potentially more complex mechanisms for operation. The additional engineering and manufacturing considerations often lead to a notable price premium. For instance, a mid-size sedan might see a $500-$1500 difference in pricing depending on the specific sunroof or moonroof design and features.
Factors Affecting Cost
Several factors influence the price difference between these roof options. Size and complexity of the opening mechanism are key. Sunroofs, typically larger than moonroofs, require more material, more sophisticated mechanisms, and often more complex seals to maintain structural integrity and prevent leaks. Furthermore, the inclusion of features like power operation, electric sunshades, or integrated climate control systems further elevates the cost.
Value Proposition Comparison
The value proposition of a sunroof or moonroof hinges on individual needs and priorities. A sunroof offers a greater sense of openness and panoramic views, ideal for those who value natural light and a spacious feel. Conversely, a moonroof, while offering some of these benefits, might be perceived as a more practical choice, especially when considering the potential cost savings and maintaining interior space.
Resale Value Influence
Both sunroof and moonroof options can impact resale value. Generally, well-maintained vehicles with desirable features, such as sunroofs or moonroofs, often command slightly higher resale prices compared to their counterparts without these features. However, the extent of the impact varies depending on the market, the specific vehicle model, and the overall condition of the vehicle. For instance, a meticulously maintained luxury SUV with a sunroof might fetch a slightly higher price than a similar model without a sunroof.
This suggests that the perceived value of these features can influence the final sale price.
Customer Reviews and Perception
Customer feedback on sunroofs and moonroofs provides valuable insights into their practical value and overall appeal. Understanding the nuances of customer preferences helps manufacturers and consumers make informed decisions. This section analyzes customer opinions, highlighting their perceived advantages and disadvantages.
Customer Feedback Summary
Customer reviews across various platforms reveal a mixed perception of sunroofs and moonroofs. While many praise the enhanced aesthetic appeal and feeling of openness, others express concerns about potential downsides. Positive feedback often emphasizes the ability to enjoy natural light and fresh air, particularly appreciated in smaller vehicles or urban settings.
Sunroofs and moonroofs are a pretty common feature, but in electric cars, like electric cars , the need for maximizing interior space often dictates a different approach to roof design. Ultimately, the best choice for a sunroof or moonroof still comes down to personal preference and the specific vehicle.
Sunroof vs. Moonroof: Pros and Cons
Customer opinions are presented in a comparative table below. This table encapsulates the common positive and negative viewpoints expressed in customer reviews.
| Feature | Sunroof | Moonroof |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | Enhanced visibility, improved interior ambiance, increased natural light | Superior design aesthetics, easier access to fresh air, generally less expensive to install |
| Potentially improved headroom in vehicles with lower rooflines | Can be less expensive than a full sunroof, improved outward visibility | |
| Cons | Potential for increased noise levels, reduced fuel efficiency, may compromise structural integrity in certain models, potential for leaks if improperly installed | Limited access to natural light compared to a sunroof, less overall headroom, reduced headroom compared to sunroofs |
| More expensive than a moonroof | Less visibility than a sunroof, limited headroom |
Impact on Customer Satisfaction
The impact of sunroofs and moonroofs on customer satisfaction is multifaceted. Positive reviews frequently cite the enhanced interior ambiance and the feeling of spaciousness, directly contributing to higher customer satisfaction scores. Conversely, concerns about noise, cost, and practicality can negatively affect customer satisfaction. It’s crucial for manufacturers to balance these factors in their design and pricing strategies.
The combination of positive aesthetic appeal and functional benefits can significantly increase overall customer satisfaction.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of sunroofs and moonroofs is a growing consideration for consumers. Factors like material sourcing, manufacturing processes, energy efficiency, and overall lifecycle impact all play a crucial role in evaluating these features. Understanding these factors helps consumers make informed decisions, potentially aligning their purchasing choices with their environmental values.Evaluating the environmental footprint of a sunroof or moonroof involves a multifaceted approach, considering various stages of the product’s lifecycle.
From raw material extraction to manufacturing, installation, use, and eventual disposal, each stage contributes to the overall impact. This evaluation also extends to the energy consumption during the vehicle’s operation, reflecting the efficiency of the chosen design.
Material Consumption and Weight
The weight and materials used in sunroof and moonroof construction directly affect the vehicle’s overall environmental impact. A lighter roof design, achieved through the use of advanced materials, reduces the energy required for manufacturing and transportation, leading to a smaller carbon footprint.
- Sunroofs typically use a combination of aluminum, steel, and glass, with variations in the specific alloys and glass types impacting the overall weight and material consumption. Different production techniques can also influence the environmental impact. For instance, using recycled materials in the manufacturing process significantly reduces the need for extracting new resources.
- Moonroofs often employ similar materials but may utilize lighter-weight alloys or specialized glass formulations. The smaller surface area of a moonroof compared to a sunroof generally leads to lower material consumption, resulting in a reduced environmental footprint.
Energy Efficiency Implications
The energy efficiency implications of sunroofs and moonroofs relate to their impact on the vehicle’s overall energy consumption. The insulation properties of the roof play a significant role, influencing the amount of heat that is lost or gained.
- Sunroofs, due to their larger opening area, can lead to increased heat loss or gain, depending on the climate and time of year. Insulated glass and specialized coatings can mitigate these effects, but the larger surface area inherently presents a greater challenge to maintaining a stable interior temperature.
- Moonroofs, with their smaller opening, have a more limited impact on the vehicle’s energy efficiency compared to sunroofs. This reduced impact on energy efficiency is often balanced by the reduced material consumption.
Summary of Environmental Impact Considerations
This table summarizes the key environmental impact considerations for sunroofs and moonroofs:
| Characteristic | Sunroof | Moonroof |
|---|---|---|
| Material Consumption | Higher due to larger surface area | Lower due to smaller surface area |
| Weight | Generally heavier | Generally lighter |
| Energy Efficiency | Potentially lower due to larger surface area | Potentially higher due to smaller surface area |
| Manufacturing Impact | Greater energy consumption | Reduced energy consumption |
| Lifecycle Impact | Potentially higher overall impact | Potentially lower overall impact |
Safety Considerations
Sunroofs and moonroofs, while enhancing vehicle aesthetics and interior comfort, introduce specific safety considerations that drivers and owners should understand. Proper understanding of these aspects ensures responsible use and helps mitigate potential risks.Careful design and construction, along with adherence to safety standards, are crucial for minimizing hazards associated with these features. The integrated safety features, particularly in the glass and reinforcement components, play a vital role in protecting occupants in the event of an accident.
Safety Features Integrated into Design
Sunroofs and moonroofs incorporate various safety features to minimize potential risks. These features are often integrated into the design process, with specific focus on the glass and its surrounding structural components. For instance, tempered safety glass is a common feature, designed to break into relatively harmless pieces upon impact, reducing the risk of severe injuries. Furthermore, reinforced frames and support structures are engineered to withstand stress and prevent catastrophic failures during collisions.
Potential Risks and Hazards
While designed with safety in mind, sunroofs and moonroofs can present certain risks. A compromised or damaged seal around the opening can allow water infiltration, potentially causing damage to the vehicle’s interior and affecting the structural integrity of the roof. Furthermore, the weight of the glass and the structural components around it can increase the overall vehicle’s center of gravity.
This shift can potentially impact handling and stability, particularly at higher speeds or during maneuvers. These considerations must be taken into account when evaluating the safety implications of sunroof or moonroof installation.
Role of Safety Glass and Reinforcement
Safety glass, a crucial component in sunroof and moonroof systems, is engineered to enhance occupant safety. It’s designed to fracture into relatively harmless, small pieces upon impact, preventing large shards that could cause serious injury. The reinforcement materials surrounding the glass, such as metal frames and supporting structures, are meticulously designed to maintain structural integrity during impacts. These features significantly reduce the potential for injury and mitigate the severity of potential accidents.
For instance, the type of glass and its reinforcement design are critical factors that are taken into account during the manufacturing and testing phases of sunroof and moonroof production.
Best Practices for Safe Operation and Maintenance
Proper maintenance is essential to maintain the safety features and performance of sunroofs and moonroofs. Regular inspections of the seals and glazing are crucial to identify any signs of damage or deterioration. Any damage, including cracks or gaps in the seal, should be addressed immediately to prevent water infiltration and potential structural problems. Additionally, avoiding excessive force or impact on the glass or frame is vital to prevent accidental breakage.
This is particularly important when cleaning or performing maintenance activities near the opening. Furthermore, following the manufacturer’s recommendations for safe operation, including restrictions on certain speeds or driving conditions, can help prevent accidents.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, choosing between a sunroof and a moonroof involves a careful consideration of personal preferences and vehicle requirements. The subtle differences in design, functionality, and cost can significantly impact the overall ownership experience. This comparison provides a solid foundation for informed decisions.
FAQ Overview: Sunroof Vs Moonroof
What are the typical price differences between sunroofs and moonroofs?
The price difference often depends on the specific vehicle model and manufacturer. Generally, sunroofs tend to be slightly less expensive than moonroofs, though variations exist.
How do sunroofs and moonroofs impact a car’s resale value?
Both features can positively influence resale value, but the extent depends on the market and specific vehicle. Features like power operation and size are key factors.
What are some common misconceptions about these features?
A common misconception is that they significantly impact fuel efficiency. While there might be a minor impact, it’s often negligible.
Which option offers better ventilation?
Both can enhance ventilation, but a sunroof’s larger opening often leads to better air circulation.





