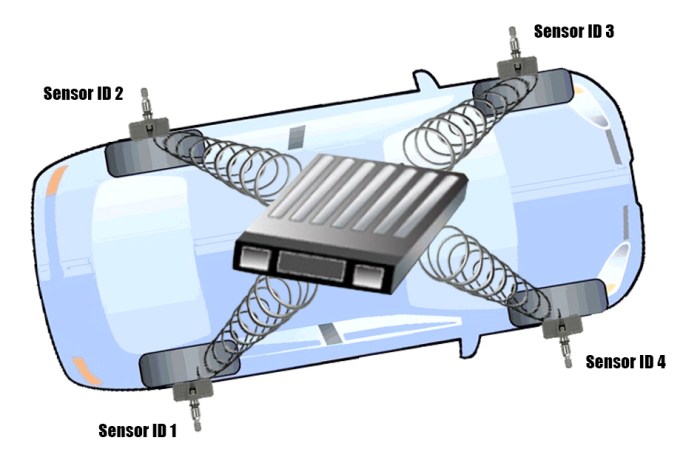
TPMS (tire pressure monitoring system) is a crucial component in modern vehicles, ensuring optimal performance and safety. It monitors tire pressure continuously, providing drivers with real-time information about their tires. This technology has evolved significantly, offering various types and functionalities. Understanding TPMS is key to maintaining safe and efficient driving.
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of TPMS, from its fundamental workings to its impact on fuel efficiency and environmental considerations. We’ll delve into the different technologies, maintenance procedures, and the role TPMS plays in modern vehicle safety.
TPMS and Fuel Efficiency
Proper tire inflation is crucial for optimal vehicle performance and fuel economy. A well-maintained tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) plays a significant role in achieving these goals. This section will delve into the intricate relationship between tire pressure, fuel consumption, and the impact of TPMS on overall vehicle performance.Maintaining the correct tire pressure is fundamental to maximizing fuel efficiency.
Under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, leading to higher fuel consumption. Conversely, tires that are over-inflated also contribute to increased fuel consumption, albeit through a different mechanism. A well-calibrated TPMS system allows drivers to quickly identify and correct these issues, thus minimizing the impact on fuel economy.
TPMS, or tire pressure monitoring systems, are crucial for vehicle safety. Modern advancements like AI-powered dash cam technology ( AI-powered dash cam ) can further enhance this, potentially providing real-time alerts about tire pressure, alongside other crucial driving data. Ultimately, reliable TPMS remains a vital part of any driver’s safety toolkit.
Impact of Tire Pressure on Fuel Consumption
Tire pressure directly affects fuel efficiency. Under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, meaning the tires deform more during each rotation, requiring more energy from the engine to propel the vehicle. This extra energy translates to higher fuel consumption. Conversely, over-inflated tires also increase rolling resistance, although to a lesser degree. This is due to a reduction in tire contact area with the road surface.
TPMS Contribution to Fuel Economy, TPMS (tire pressure monitoring system)
A properly functioning TPMS system allows drivers to maintain optimal tire pressure. Early detection of under-inflation is key to preventing significant fuel loss. This proactive approach enables drivers to address the issue promptly, thus reducing the amount of extra fuel consumed over time. Maintaining the correct tire pressure, as monitored by TPMS, ensures that the tires are in their optimal operating range.
How TPMS Improves Fuel Efficiency
A well-maintained TPMS system helps in preserving fuel efficiency by enabling drivers to:
- Identify under-inflation early, before significant fuel consumption increases.
- Avoid the extra fuel expenditure associated with driving on under-inflated tires.
- Maintain optimal tire pressure, which minimizes rolling resistance.
- Achieve better fuel economy over the vehicle’s lifespan.
TPMS Impact on Overall Vehicle Performance
Beyond fuel efficiency, TPMS contributes to overall vehicle performance in several ways. Correct tire pressure directly affects handling, braking, and steering responsiveness. Under-inflation can lead to poor handling and increased braking distances, while over-inflation can make the vehicle feel less stable. A TPMS system helps to mitigate these issues by promptly alerting drivers to tire pressure discrepancies, allowing them to rectify the problem quickly.
This proactive approach contributes to the safety and comfort of the driving experience.
- TPMS enhances safety by preventing tire failure, which can lead to dangerous situations.
- TPMS improves handling by maintaining optimal tire contact with the road surface, enhancing vehicle stability.
- TPMS reduces wear and tear on tires by preventing uneven tire wear caused by under- or over-inflation.
TPMS and Environmental Impact

Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) contribute significantly to a more sustainable transportation future. By optimizing tire pressure, TPMS directly impacts fuel efficiency and reduces harmful emissions, ultimately lessening the environmental footprint of vehicles. This positive impact aligns with global efforts towards reducing carbon emissions and promoting eco-friendly practices in the automotive industry.
Environmental Benefits of TPMS
TPMS promotes fuel efficiency by ensuring optimal tire pressure. Properly inflated tires reduce rolling resistance, leading to decreased fuel consumption. This directly translates to lower emissions of greenhouse gases, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier environment. Reduced fuel consumption also translates to reduced reliance on fossil fuels, a crucial step towards a more sustainable energy future.
Optimized Tire Pressure and Fuel Consumption
Maintaining the correct tire pressure is crucial for fuel efficiency. Under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, requiring the engine to work harder to propel the vehicle. This increased effort translates to higher fuel consumption and increased emissions. Conversely, properly inflated tires minimize rolling resistance, enabling the engine to operate more efficiently, thereby lowering fuel consumption and emissions. For instance, a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) found that properly inflated tires can improve fuel economy by up to 3%.
TPMS and Sustainable Transportation
TPMS plays a critical role in sustainable transportation by directly contributing to reduced fuel consumption and emissions. By promoting the use of vehicles with optimal tire pressure, TPMS contributes to a significant reduction in the overall environmental impact of transportation. This contributes to the overall goal of a more sustainable transportation system, a key component of global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Comparison of Environmental Impact
| Feature | Vehicle with TPMS | Vehicle without TPMS |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher, due to optimized tire pressure | Lower, due to under-inflated tires |
| Emissions (CO2, etc.) | Lower, resulting from improved fuel economy | Higher, due to increased fuel consumption |
| Tire Wear | Lower, due to even tire wear | Higher, due to uneven tire wear |
| Overall Environmental Impact | Lower, leading to a more sustainable transportation footprint | Higher, leading to a larger carbon footprint |
The table highlights the tangible environmental benefits associated with vehicles equipped with TPMS. Vehicles with TPMS demonstrate a positive impact on fuel efficiency and emissions, resulting in a smaller environmental footprint.
TPMS Cost and Value Proposition
Tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) are increasingly becoming standard equipment on vehicles, but their initial cost can vary significantly. Understanding the comparative costs and the long-term benefits is crucial for assessing the value proposition of this technology. This analysis will explore the cost variations across vehicle types, the long-term financial advantages of a functional TPMS, and the return on investment (ROI) considerations.
TPMS, or tire pressure monitoring systems, are crucial for vehicle safety. They constantly monitor tire pressure, which is essential for optimal performance and fuel efficiency. A good alternative for powering these systems, and other vehicle accessories, is a solar-powered car charger. Solar-powered car charger solutions can significantly reduce reliance on traditional charging methods, making them environmentally friendly and potentially cost-effective in the long run.
Ultimately, maintaining proper tire pressure through a reliable TPMS is key to safe driving.
Comparative Analysis of TPMS Costs Across Vehicle Types
Different vehicle types, from compact cars to large SUVs and trucks, have varying TPMS costs. Factors influencing these differences include the complexity of the system, the technology employed (e.g., tire pressure sensors, wheel speed sensors), and the manufacturer’s pricing strategy. Premium vehicles often incorporate more sophisticated TPMS systems, which can lead to higher initial costs.
Long-Term Cost Benefits of a Properly Functioning TPMS
A properly functioning TPMS offers several long-term cost benefits. These benefits include reduced fuel consumption, which directly translates to lower fuel costs over time. Furthermore, the system helps prevent premature tire wear, reducing the need for frequent tire replacements and associated labor costs. By alerting drivers to potential tire problems, TPMS can also prevent costly repairs and potential accidents caused by underinflated or overinflated tires.
Return on Investment (ROI) for Implementing TPMS
The return on investment for a TPMS is multifaceted and can be calculated by assessing the potential savings in fuel, tire replacements, and repairs. For instance, a vehicle experiencing consistent underinflation may see significant fuel consumption increases and substantial tire wear. The TPMS intervention can significantly reduce these costs over the vehicle’s lifespan. This return on investment often becomes more evident over the vehicle’s extended lifespan.
Comparison of TPMS Costs with Potential Tire-Related Repairs
| Cost Category | TPMS Initial Cost (Example) | Potential Tire Repair Costs (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| TPMS Installation | $100-$300 (depending on vehicle type and complexity) | $100-$500+ (depending on the extent of damage) |
| TPMS Maintenance (e.g., sensor replacement) | $50-$200 (every 5-10 years, depending on sensor technology) | $50-$500+ (depending on the extent of damage and the required repairs) |
| Tire Replacement | N/A (Indirectly reduced by TPMS) | $100-$500+ (per tire) |
| Fuel Savings | N/A (Indirectly improved by TPMS) | N/A |
The table above provides a basic illustration of potential cost comparisons. The actual figures can vary considerably based on the specific vehicle, tire type, driving conditions, and maintenance practices. It is essential to consider these factors when evaluating the long-term cost-effectiveness of a TPMS.
Conclusion
In conclusion, TPMS is more than just a technological advancement; it’s a vital safety feature that contributes to fuel efficiency and environmental sustainability. By understanding its various aspects, drivers can optimize their vehicle performance and contribute to safer roads. Maintaining proper tire pressure is key, and TPMS simplifies this process. We hope this guide has provided valuable insights into this critical automotive technology.
Questions and Answers: TPMS (tire Pressure Monitoring System)
What are the common causes of TPMS malfunctions?
Common causes of TPMS malfunctions include faulty sensors, damaged wiring, or issues with the receiver unit. Poor sensor installation, or a damaged tire itself can also contribute to problems.
How often should TPMS sensors be replaced?
TPMS sensors typically have a lifespan of 5-7 years. However, this can vary depending on the specific sensor model and driving conditions. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for manufacturer recommendations.
What are the benefits of using TPMS?
TPMS offers several benefits, including improved fuel efficiency, enhanced safety by preventing tire-related incidents, and providing drivers with real-time information about their tire pressure. Proper tire inflation also helps maintain the vehicle’s handling and ride quality.
Can TPMS be installed on older vehicles?
Yes, TPMS systems can often be retrofitted onto older vehicles. However, the specific process and availability may vary based on the vehicle model and year. Consult a qualified mechanic or dealer for advice.